- Saviynt Forums
- Saviynt Exchange
- Community Sourced Integrations
- Celonis Integration Guide
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Notify a Moderator
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Notify a Moderator
on
02/02/2024
12:30 AM
- edited on
04/04/2024
09:08 AM
by
![]() Rishi
Rishi
Disclaimer
The integration was created by Saviynt community users.. The integration is available “as is” and falls under standard connectors support for REST, SOAP, JDBC, LDAP, PowerShell, Jar, and Saviynt Connector Framework.
Preface
This guide describes the integration between Saviynt Enterprise Identity Cloud (EIC) and Celonis.
Audience
This guide is intended for administrators and target application integration teams responsible for implementing a secure integration service with Celonis.
Introduction
Celonis is a Process Mining & Task Mining Tool, It does this by Connecting source system data to achieve the following Insights generation into. Process improvements improved cycle time, rework efficiency benefits, & automation opportunities. Process visibility telling the story through facts and data to improve the process for the business & GBS. Process optimization & improved business processes and customer experience.
The Celonis connector enables you to seamlessly integrate with Celonis to manage the user lifecycle and govern access to their accounts and workspaces.
For more information about different connectors in EIC, see Connectors Documentation.
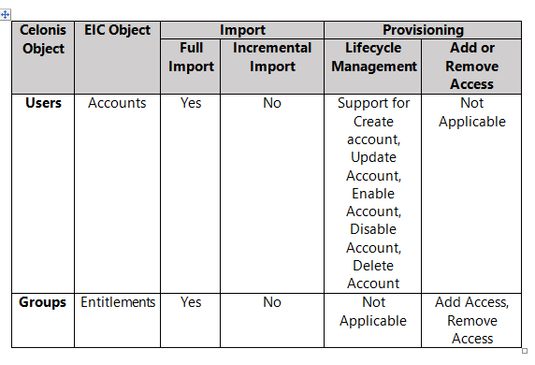
Supported Features
The Celonis integration supports the following features:
Supported Software Versions
Software | Version |
EIC | Release v4.5 and later |
Understanding the Integration between EIC and Celonis
You must create an integration between EIC and the collaboration platform hosted by the target application to perform import, provisioning, and de-provisioning tasks. The following components are involved in the integration:
Objects are imported as entitlement types into EIC.
Security System represents the connection between EIC and the target application.
It comprises an endpoint, which is the target application for which you want EIC to manage the identity repository.
It provides application instance abstraction from connectivity including high-level metadata. For more information about creating a security system, see Creating a Security System.
- Endpoint is an instance of an application within the context of a security system.
It is the target application or application from which the connector imports the data and performs provisioning or de-provisioning of identity objects, such as users, accounts, and entitlements.
It is mandatory to create an endpoint after creating the security system.
You can associate a single security system with multiple endpoints if the deployment involves modeling multiple isolated virtual applications (based on sets of specific entitlements according to certain categories) within a single application instance. For more information about creating an endpoint, see Creating an Endpoint for the Security System.
The connector is a software component that enables communication between EIC and the target application. It provides a simplified integration mechanism where in some instances you only need to create a connection with minimal connectivity information for your target application. The REST connector is used for importing, provisioning accounts, and accessing through the REST APIs. For more information about creating a connection, see Creating a Connection.
Job Scheduler is a software component that executes a job based on the configured schedule to perform import or provisioning operations from EIC.
When a provisioning job is triggered, it creates provisioning tasks in EIC. When these tasks are completed, the provisioning action is performed on the target application through the configured connector. If you want to instantly provision requests for completing the tasks without running the provisioning job, you must enable Instant Provisioning at the security system level and the Instant Provisioning Tasks global configuration. For more information about the jobs used by the connectors in the Celonis integration.
Integration Approach
- Standard REST connector using SCIM protocol is used to connect Celonis application to Saviynt
- REST API calls are made through REST connector to execute multiple operations (i.e. import account/ import access/ create account/ add access/ enable account/ disable account/ Update account/ remove access/ delete account)
- The REST integration enables you to gain visibility, manage user life cycle, and govern access for the data available in the REST endpoint.
Account reconciliation
- Saviynt is importing all the user accounts from Celonis.
Below are the account attributes details which are getting imported from Celonis.
Celonis Account Attribute | Saviynt Account Attribute |
userName | name |
id | accountID |
active | status |
displayName | displayName |
active | customproperty1 |
Access reconciliation
- Saviynt is importing all Groups (entitlements) from Celonis.
Below are the entitlement attribute details which are imported from Celonis into Saviynt.
Celonis Entitlement Attribute | Saviynt Entitlement Attribute |
id | entitlementID |
displayName | entitlement_value |
displayName | displayName |
urn:celonis:params:scim:schemas:extension:2~dot#0:Group.role | entitlement_glossary |
Setting Up the Integration
Creating API keys
Using API keys is an effective and secure method of communicating between your and external systems, such as an identity provider. They are created within an individual user profile in your Celonis Platform, with the key’s permissions mirroring those of the user who created them.
For security reasons, an API key is only displayed at the time it is created. Therefore you must create a new key if you no longer have access to any you create.
Using an API key is one of the methods involved in configuring SCIM API (for provisioning and deprovisioning users and groups in your ), with the alternative being creating and granting permissions to application keys.
Admins can also receive a system notification whenever an admin creates or deletes an API key. See: System notifications
Procedure
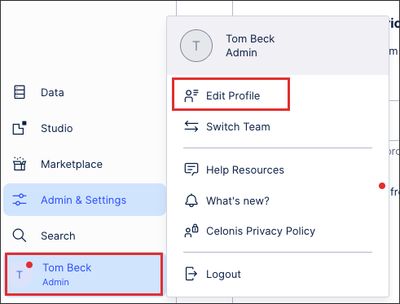
To create an API key as an admin:
- Click your profile and select Edit Profile.
|
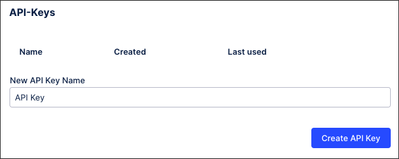
- Enter a new API key name and click Create API Key.
- Copy the API key displayed.
Note:You can only view an application key once, so make sure to copy it when you create it. If you don't have a copy of the keys on your list, you'll need to create a new one.
- Add the API key to the authorization header of your requests using the following format:
| Authorization: Bearer API_KEY |
Creating a Connection
Connection refers to the configuration setup for connecting EIC to target applications. For more information about the procedure to create a connection, see Creating Connections.
Understanding the Configuration Parameters
While creating a connection, you must specify connection parameters that the connector uses to connect with the target application, define the type of operations to perform, the target application objects against which those operations are performed, and the frequency of performing them. In addition, you can view and edit attribute mappings between EIC and the target application, predefined correlation rules, and provisioning jobs and import jobs.
Importing Connection Package
The Connection Package helps you build the connection with pre-defined JSONs, this can be used if your tenant does not already have out of the box connection templates available. Here are the steps to import the Celonis connection package.
- Download the connection package.
- Navigate to Admin → Transport → select Import Package.
- Browse the downloaded package and Import.
- Navigate to Admin → Connections → Select “Celonis ” Connection.
- Edit the connection with your CelonisTenant Details.
Connection JSON:
The connection JSON cannot be embedded in the Connection Package. Hence attaching the Connection JSON separately
The connection JSON cannot be embedded in the Connection Package. Hence attaching the Connection JSON separately
| { "authentications": { "userAuth": { "authType": "oauth2", "url": "", "httpMethod": "POST", "httpParams": {}, "httpContentType": "application/json", "expiryError": "ExpiredAuthenticationToken", "authError": [ "InvalidAuthenticationToken", "AuthenticationFailed" ], "retryFailureStatusCode": [ 400, 401, 403, 500, 502 ], "timeOutError": "", "errorPath": "error", "maxRefreshTryCount": 5, "tokenResponsePath": "", "tokenType": "Bearer", "myappkey": "AppKey<Please enter Celonis PROD App Key>" } } } |
Creating a Security System
The security system represents the connection between EIC and the target application. For more information on creating a security system, see Creating a Security System.
Creating an Endpoint for the Security System
Endpoint refers to the target application used to provision accounts and entitlements (access). For more information on creating an endpoint, see Creating Endpoints..
Using the Celonis Integration
You can use the Celonis integration for performing import and provisioning operations after configuring it to meet your requirements.
Guidelines for Using the Integration
You must apply the following guidelines for configuring import:
- Run account import before running the access import.
- Map all Celonis attributes to EIC account attributes using ImportAccountEntJSON.
- Use Java ternary operators if you want to add conditions in the provisioning parameters. You can use Java operations to tweak any attributes by using if-else conditions, substrings, or operators in the JSON for provisioning.
Configuring Import Operations
- Full account import: When configuring the connection for the first time, first perform full import to import all existing accounts from the target application to EIC. To perform full import, the invoke API gets response from the target application and maps the attributes in the target application with attributes in EIC. As part of this process, the deleted accounts are also identified and marked as suspended from import service.
- Full Access import: When configuring the connection for the first time, first perform full import to import all existing access from the target application to EIC. To perform full import, the invoke API gets response from the target application and maps the attributes in the target application with attributes in EIC. As part of this process, the deleted entitlements are also identified and marked as inactive.
The import jobs are automatically created in EIC after you create a connection for the Celonis integration. For more information about creating jobs, see Data Jobs.
Importing Accounts and Accesses
You must import accounts after the users are available in EIC.
To import accounts:
- Specify the connection and import parameters. For more information, see Account and Access import.
Note: Ensure that the connection type is selected as REST. - Configure the Application Data Import (Single Threaded) / Application Data Import (Multi-Threaded) job to import accounts and access. For more information, see Data Jobs.
Configuring Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Provisioning is automatically enabled when a connection is configured. For detailed information about performing provisioning tasks, see Access Request System.
To provision objects to the target application:
- Specify the connection and provisioning parameters. For more information, see Configuration Parameters for Provisioning.
Note: Ensure that the connection type is selected as REST. - Configure the Provisioning job (WSRETRY). For more information, see Provisioning Jobs.
When a provisioning job is triggered, it creates provisioning tasks in EIC. When these tasks are completed, the provisioning action is performed on the target application through the connector.
Troubleshooting
To troubleshoot common problems with connectors, answer frequently asked questions, and provide solutions to a few common issues you might encounter while configuring or working with connectors, see Common Troubleshooting Guide for Connectors.
To troubleshoot common problems or obtain answers for frequently asked questions for REST connectors, see the REST Connector Guide.